在 GeneGlobe 配置
寻找或定制设计合适的靶标特异性检测和组合,以研究您感兴趣的生物靶标。
Microbial DNA qPCR Assay
Cat. No. / ID: 330025
One 100 µl tube Microbial DNA qPCR Assay, one 1.35 ml tube Microbial qPCR Mastermix
登录 要查看您的账户定价。
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays 旨在用于分子生物学应用。这些产品不能用于疾病诊断、预防和治疗。
在 GeneGlobe 配置
寻找或定制设计合适的靶标特异性检测和组合,以研究您感兴趣的生物靶标。
特点
- 经实验验证,具有高度灵敏性和特异性
- 可检测微生物物种、毒力因子基因、或抗生素耐药性基因
- 简单便利的qPCR工作流程
产品详情
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays含有两种PCR引物(每种10 µM)、以及一种5'水解探针(5 µM)用于定量real-time PCR。Microbial DNA qPCR Assays采用经实验验证的专有技术,其PCR效率高,扩增效果准确、稳定。所有的Microbial DNA qPCR Assay都经过严格的实验验证,PCR反应效率高。该产品搭配Microbial qPCR Mastermixes和Microbial DNA-Free Water使用,可确保PCR的高效率。
绩效
最低定量阈限(LLOQ)
LLOQ是指在标准曲线线性范围内的最低模板浓度(参见 Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification)。所有Microbial DNA qPCR Assays中的93%具有低至100个基因拷贝的LLOQ(参见 The LLOQ for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity)。该系列产品中的92%微生物检测产品能达到这一LLOQ,95%的毒力因子检测产品和97%的抗生素耐药性基因检测产品能达到这一LLOQ(参见 The LLOQ for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity、 The LLOQ for virulence factor genes Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity和 The LLOQ for antibiotic resistance genes Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity)。特异性
所有Microbial DNA qPCR Assay都经过严格检验,确保能够灵敏检测某一物种或基因(参见 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific)。对于能够检测一种以上五种或基因的产品,产品说明页上附有电脑预测可检测靶标的列表。即便样本中存在多种物种,该试剂盒仍有极高的检测特异性,此类样本包括粪便、痰和菌斑(参见 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples)。
查看图表
Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification.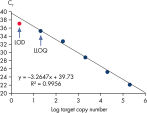 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.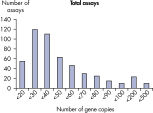 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.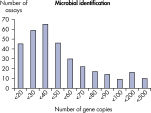 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.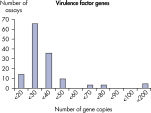 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.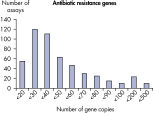 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.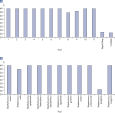 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.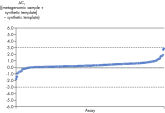
 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific. Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.
原理
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays在进行物种检测时,可检测细菌的16S rRNA基因和真菌核糖体rRNA基因序列;采用PCR扩增引物和水解探针,检测毒力因子基因和抗生素耐药性基因。
程序
Microbial DNA qPCR Assay的实验流程简单,能够在各种real-time PCR仪上使用。使用相应的QIAamp试剂盒从样本中分离DNA,然后使用与PCR仪相应的Supplemental Microbial qPCR Mastermix构建PCR反应体系。为每种样本构建4个独立的PCR反应体系,包括Positive PCR Control、No Template Control、Microbial DNA Positive Control以及Microbial DNA qPCR Assay。进行real-time PCR,然后使用在线数据分析软件或Excel模板文件进行数据分析。
应用
Microbial DNA qPCR Assay高度适用于细菌或真菌物种检测,以及微生物的抗生素耐药性基因或毒力因子检测,适用样本包括粪便、痰、阴道拭子、污水等等。
辅助数据和图表
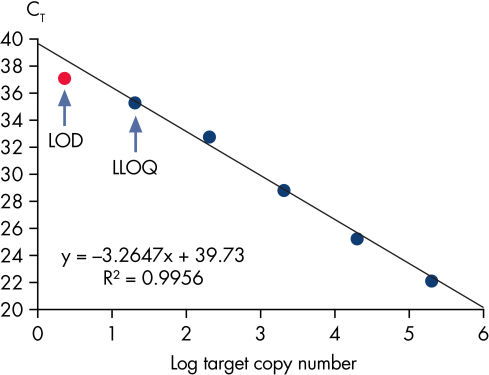
Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification.
This chart demonstrates the difference between the limit of detection (LOD) and the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ). The LOD is defined as the lowest concentration at which 95% of the positive samples are detected, whereas the LLOQ is the lowest concentration that falls within the linear range of a standard curve. LOD depends upon the precision of the assay, and requires at least 40 replicates for determination of a positive sample. For the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays, LLOQ is sufficient to determine assay sensitivity.
资源
安全数据表 (1)
产品介绍与指南 (2)
学术海报 (1)
技术资讯 (2)
试剂盒操作手册 (1)
Safety Data Sheets (1)
Certificates of Analysis (1)
FAQ
What species are detected by the Pan Bacteria 1 and Pan Bacteria 3 Assays?
What sequences are used to design the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What are the storage conditions for the Microbial DNA qPCR products?
What is the difference between LLOQ and LOD?
What is the difference between Positive PCR Control (PPC) and Microbial DNA Positive Control?
Is the Microbial qPCR mastermix used in the Microbial DNA assay and in the Microbial DNA arrays free of genomic bacterial DNA?
Can I multiplex the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What sample types can be tested on the arrays/assays?
Can I measure antibiotic resistance gene expression?
What is the expected amplicon size of the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What is LLOQ?
Can I measure virulence factor gene expression?
Can I use the Microbial DNA-Free Water and Microbial qPCR Mastermix if they have been opened more than 3 times?
How can I calculate the number of bacterial cells that are present in a sample using the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
Are the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays wet-lab verified?
Are the assays species-specific?
Which Microbial qPCR Mastermix should I use?
What are the minimum sample requirements for Microbial DNA qPCR kits?
Which probe labels are available for the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What is the sensitivity for the Microbial DNA qPCR kits?

