QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit – RNA Extraction from Blood
从新鲜的全血样本中纯化胞内RNA
从新鲜的全血样本中纯化胞内RNA
✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
Cat. No. / ID: 52304
✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
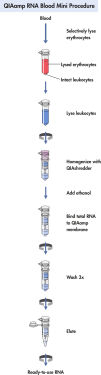
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit使用硅胶膜,可从多至1.5 ml的人类新鲜全血中纯化胞内RNA。可以使用常规的抗凝剂如柠檬酸盐、肝素或EDTA等稳定血液样本。使用QIAshredder离心柱对样本进行均化处理后进行快速离心,从而简化了纯化RNA的流程。可在QIAcube全自动核酸纯化仪上全自动完成纯化处理。
QIAamp纯化流程可完全去除RNases、污染物和酶抑制剂,制备的高品质RNA适用于多种下游应用(参见" High-quality RNA for northern analysis"和" Reliable RT-PCR analysis")。
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit制备的RNA品质高,含有最少量的DNA。RNA的纯化不可避免存在DNA污染。但对于某些痕量DNA敏感的RNA应用则必须去除残留的DNA,对于这些应用,QIAGEN RNase-Free DNase Set(可选购)为QIAamp RNA纯化流程提供简便的柱上DNase酶处理操作,去除残留DNA。
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit使用硅胶膜技术纯化细胞RNA,无需苯酚-氯仿抽提。RNA特异性结合到QIAamp硅胶膜上,污染物流出。通过两步高效洗涤完全去除二价阳离子和蛋白质等PCR抑制剂,再用水或试剂盒中的缓冲液洗脱结合在离心柱上的纯DNA。
QIAamp技术从新鲜的全血样本或其他样本来源中纯化的总细胞RNA,可即时用于PCR和印迹实验中。QIAamp样本制备技术完全得到验证认可。
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit可从多至1.5 ml的新鲜人体全血中纯化细胞RNA。可以使用常规的抗凝剂如柠檬酸盐、肝素或EDTA等稳定血液样本。也可从组织样本中纯化得到总细胞RNA。
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | PCR, real-time PCR, microarray |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl |
| Main sample type | Whole blood, tissue |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | Cellular RNA |
| Sample amount | 50–1.5 ml |
| Format | Spin columns |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation) |
| Time per run or per prep | <1 hour |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Yield | 1–5 µg |