QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 27204
特点
- 质粒 DNA 质量和性能与 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 相同
- 与 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 相比,可减少多达 22% 的塑料和多达 14% 的纸板
- 由 100% 消费后再生塑料制成的重复使用型废液管
- 缓冲浓缩液比标准缓冲液少用 93% 的塑料
产品详情
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 是标准 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 的环保型版本。QIAwave Kit 比我们的标准试剂盒少用多达 22% 的塑料和 14% 的纸板,并提供由 100% 消费后回收塑料制成的废液管,您可以在整个过程中重复使用。QIAwave 缓冲液为浓缩液,每瓶可减少 93% 的塑料用量。为节省纸张,试剂盒中没有印刷的方案。您可以从资源列表中下载方案,或扫描试剂盒包装盒内的二维码。虽然我们的 QIAwave Kit 包装和组件看起来有所不同,但其与我们的标准试剂盒一样易于使用,化学成分和性能也完全相同。
请注意,您需要无菌玻璃瓶来储存重组缓冲液。
我们还与 My Green Lab 合作,评估了该试剂盒对环境的影响。My Green Lab ACT 标签旨在根据若干可持续性标准对产品进行评估和评分。其中包括:
• 制造
• 负责任的化学品管理
• 产品和包装材料中的可持续内含物
• 包装报废时的处置
除能耗和水耗分别按每 kWh 或每加仑 1 分计分外,其他产品均按 1-10 分计分。分数低意味着对环境的影响较小 – 见图“QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit ACT 环境影响因子标签 US 50/ 250、EU 50/ 250 和 UK 50/ 250”)。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 设计用于在常规分子生物学应用中分离最多达 20 μg 高纯度质粒或柯斯质粒 DNA,如荧光和放射性测序和克隆。使用 QIAprep 高产补充方案可以获得更高的产量(可达 30 μg)。建议将此试剂盒与 QIAvac 24 Plus 一起使用,以获得最佳结果。
查看图表
 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
绩效
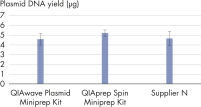
因为化学成分相同,所以 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 和 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 性能相同。我们还表明,这两款试剂盒的性能均优于竞争对手的试剂盒(见图“ QIAwave Kit 性能”)。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 能够在常规分子生物学应用中纯化最多达 20 ug 分子生物学级质粒 DNA 或柯斯质粒 DNA,如 PCR、测序和克隆。
QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns 用途广泛,您可以将其用于微型离心机、真空歧管或 QIAcube Connect 上(见图“QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column 处理选项: 微型离心机、 真空歧管和 自动化系统”)。真空程序使处理更简单,样本处理更快捷。QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column 也可用 QIAvac 24 Plus 或任何其他带有鲁尔接头的商用歧管进行真空处理。
| 格式 | 离心柱 |
| 纯化模块 | QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column |
| 通量 | 1–24 个样本 |
| 制备时间 | 30 分钟内完成 24 个小提 |
| 所需设备 | 微型离心机或真空歧管;使用 QIAcube Connect 进行全自动运行 |
| 裂解物澄清 | 离心 |
| 柱储液罐容量 | 800 µL |
| 最小洗脱缓冲液体积 | 50 µL |
| 高拷贝质粒培养容量 | 1–5 mL |
| 低拷贝质粒/科斯质粒培养容量 | 1–10 mL |
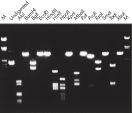
纯化得到的 DNA 可用于限制性酶切(参见图“ 用各种限制性内切酶进行完全酶切”)。
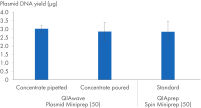
我们还比较了使用 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) 缓冲液和 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50) 标准缓冲液通过倾倒或移液方式获得的质粒 DNA 产量。如图“ 缓冲浓缩液的处理”所示,两种方法的产量相当。
查看图表
原理
QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column 含独特的硅胶膜,在高浓度离液盐中可结合多达 20 μg DNA,然后用少量低盐缓冲液洗脱。QIAprep 膜技术去除了耗时的苯酚/氯仿提取和乙醇沉淀,并解决了树脂松散和稀浆带来的问题与不便。从 QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column 洗脱得到的高纯度质粒 DNA 可直接使用,无需沉淀、浓缩或脱盐。
程序
使用 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep 进行 DNA 质粒纯化只需简单的结合-洗涤-洗脱程序(参见流程图“ QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep 程序”)。
1.使用离心法裂解细菌培养物并清除裂解物。
2.将清除的裂解物加入 QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column。此时,质粒 DNA 吸附在硅胶膜上,杂质被洗去。
3.然后,用少量洗脱缓冲液或水洗脱,得到纯 DNA。
除了从 E. coli 纯化得到质粒外,QIAwave Plasmid Mini Kit 还可以用于从 Saccharomyces cerevisiae、Bacillus subtilis 和 Agrobacterium tumefaciens 中纯化得到质粒 DNA。如果您需要获取相关应用的实验方案,请与 QIAGEN 技术服务团队或您的本地经销商联系。
QIAwave 缓冲液是浓缩液,您可以通过加水和/或乙醇方便地重新配制;详情请查阅手册。QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column 和 Waste Tube 为独立包装袋,需要在开始实验方案前预先组装。这需要多花一点时间,但确实减少了塑料垃圾。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 可在 QIAcube Connect 上使用 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 实验方案进行自动操作。
查看图表
应用
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit 可重复提取高纯度 DNA,以适合用于大多数应用,包括:
- PCR
- 限制性酶切
- 连接和转化
- 测序
- 筛选
辅助数据和图表
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
This ACT environmental impact factor label evaluates and scores the QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) for plasmid DNA isolation on several sustainability criteria. Scores are 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which is scored as 1 point per kWh. or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) has a 36.8% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50).

Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | 荧光和放射性测序(包括毛细管测序)、连接、克隆、转化等 |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Culture volume/starting material | 1–10 ml culture volume |
| Elution volume | 50–200 µl |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or prep per run | <30 minutes |
| Yield | <150 ug |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1–24 samples per run |
| Number of preps per run | 1–24 samples per run |