qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays
Cat. No. / ID: 337812
Features
- Over 10 million assays available, targeting all regions of the genome
- Wet bench-tested assays
- Simple real-time PCR procedure
- Complimentary web-based data analysis Software
Product Details
Performance
All qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays are wet bench-tested for several characteristics affecting the accuracy of real-time PCR results: specificity, wide dynamic range, and uniformly high amplification efficiency. Laboratory verification of assay quality ensures that qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays deliver reliable results.
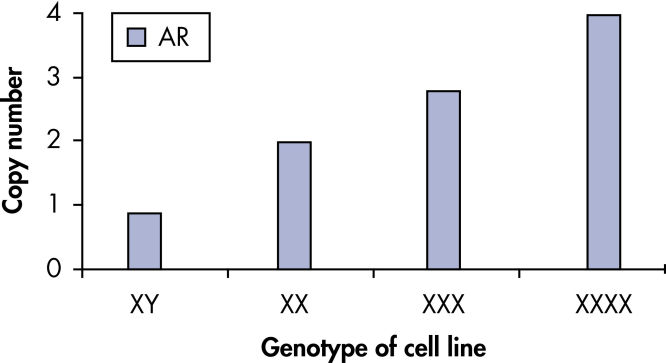
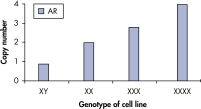
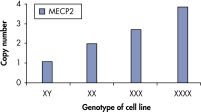
qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays accurately identified aneuploidy in cell lines containing chromosomal aberrations previously identified by cytogenetic methods. Assays for AR and MECP2, which are both on the X chromosome, correctly quantified gene copy number in cell lines with 1, 3, and 4 copies of the X chromosome.
See figures
Principle
Procedure
Applications
qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays are highly suited for accurate detection of copy number alterations or variations at individual loci using fresh, frozen, or FFPE samples.
Supporting data and figures
qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays accurately identify aneuploidy.
qBiomarker Copy Number PCR Assays accurately identify aneuploidy.