✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit
Cat. No. / ID: 674623
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Fulfills the high-quality, analytical and clinical performance standards in compliance with European Regulation 2017/746 for in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDR)
- Reliable and sensitive quantification of JAK2 V617F/G1849T allele, a major diagnostic criterion for MPN according to the WHO guidelines (1)
- An automated workflow from sample to result
- All-in-one, ready-to-use kit, including reaction mixes and internal control
- Easy-to-use protocols validated on QIAsymphony SP and automated interpretation with Rotor-Gene AssayManager v2.1
- Larsen’s primers in line with international recommendations (2)
Product Details
The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit is an in vitro molecular diagnostic kit for real-time PCR on the Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5plex HRM instrument. The kit fulfills the requirements of the European Regulation 2017/746 for in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDR). This in vitro diagnostic PCR assay is for reliable and sensitive quantitative detection of the JAK2 V617F/G1849T mutation in gDNA from human peripheral whole blood anticoagulated with K2-EDTA.
Results obtained with the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit are intended for use as an adjunct to evaluation of suspected philadelphia (ph) chromosome negative myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) and molecular disease monitoring in MPN patients. Any diagnostic results generated must be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical-pathological findings.
Performance
This is an enhanced version of the kit that has undergone a program to fulfill the IVDR requirements.
For details on the performance, refer to the “Performance Characteristics” section of the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit Handbook.
Analytical performance
To ensure improved sensitivity and reproducibility, the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit is optimized to detect the JAK2 V617F/G1849T mutation and uses prediluted plasmid standards, primers, and probe mixes in line with international technical recommendations (2). The limit of blank (LOB) measured using the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit corresponds to the expected value in a normal population (0%). The analytical sensitivity has a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.042% and the limit of quantification (LOQ) is 0.233% of the JAK2 V617F mutation.
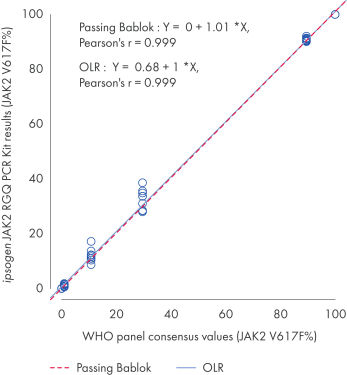
The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit was tested with WHO International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F (NIBSC, panel code 16/120[VLQ1] ). Concordance is confirmed, demonstrating the suitability of the kit in providing JAK2 V617F data that are in agreement with other commonly used diagnostic techniques (see figure “Concordance between the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit results and the WHO International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F”).
Clinical performance
The clinical performance of the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit was evaluated in a multicenter, international, prospective, interventional study with 216 participants with suspected polycythemia vera (PV). Using the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit for PV diagnosis, the sensitivity was 94.64% and the specificity was 95.62%. This demonstrates that the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit enables detection of PV in the vast majority of subjects with the disease, and helps rule out the disease in the vast majority of subjects without PV.
Principle
The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit is a ready-to-use kit for the detection and quantification of the JAK2 V617F/G1849T somatic mutation due to a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood of subjects with suspected or diagnosed MPN. The kit uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and exploits the qPCR oligonucleotide hydrolysis principle on the Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5plex HRM instrument. The kit is highly sensitive with excellent reproducibility. The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit provides 4 plasmid standard dilutions for each mutant JAK2 V617F and the wild-type JAK2 allele. Use of the standards enables accurate quantification of JAK2 V617F and JAK2 wild-type. Results are expressed as the percentage of JAK2 V617F in total JAK2, as well as mutation detection status based on the LOD.
Procedure
The first step is manual QIAamp DSP DNA Blood Mini Kit or automated QIAsymphony DSP extraction and determination of quality and quantity of genomic DNA. The second step is the amplification of DNA by real-time PCR, with all needed reagents provided in the kit. The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit detects and quantifies the JAK2 V617F/G1849T mutation on the Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5plex HRM instrument. Finally, the Rotor-Gene AssayManager software simplifies data analysis and management, and maximizes process safety for efficient and timely result reporting.
Applications
The ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit for in vitro diagnostic use enables sensitive and reliable detection and quantification of the JAK2 V617F/G1849T mutation.
For JAK2 V617F detection and quantification as an adjunct to evaluation of suspected Ph- MPN and molecular disease monitoring in MPN patients.
References:
1. Arber, D.A. et al. (2016) The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 127, 2391.
2. Jovanovic, J.V., et al. (2013) Establishing optimal quantitative-polymerase chain reaction assays for routine diagnosis and tracking of minimal residual disease in JAK2-V617F-associated myeloproliferative neoplasms: a joint European LeukemiaNet/MPN&MPNr-EuroNet (COST action BM0902) study. Leukemia 27:2032.
Supporting data and figures
Concordance between the ipsogen JAK2 RGQ PCR Kit results and the WHO International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F (NIBSC, panel code 16/120) consensus values.
Concordance was assessed using an ordinary Linear Regression (OLR) and a Passing Bablok Regression. The panel comprises seven JAK2 V617F levels: 100%, 89.5%, 29.6%, 10.8%, 1.00%, 0.03% and 0%. The WHO consensus values were determined using a range of commonly used techniques as part of an international collaborative study; the reference values attributed to each JAK2 V617F% level are median values (more information on https://www.nibsc.org).