Products
Features
- Accurate and unaffected by prior BCG vaccination (2–4)
- Efficient, with results after one patient visit (1)
- Objective results (1)
- Proven performance in immunosuppressed patients (5–8)
Product Details
Performance
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant threat to humanity, and therefore identifying TB infection is essential. A person infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but who shows no symptoms is regarded as having latent TB infection. Global organizations acknowledge that to fight TB effectively, accurate identification and treatment of latent TB infection, as well as active TB disease, are vital (9).
QuantiFERON-TB Gold (QFT) is a modern alternative to the 110 year old tuberculin skin test (or Mantoux test) and is the most studied IGRA, with over 800 published peer-reviewed publications. The test is highly accurate and unaffected by Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination (2–4).
QFT is an interferon-gamma (IFNγ) release assay, commonly known as an IGRA, and measures the cell-mediated immune response to specific TB antigens in whole blood. Patients may be tested in a single patient visit, with objective results, eliminating the need for two-step testing (1). The test has proven performance in immunosuppressed patients (5–8).
By reducing false positive results seen with TST, QFT reduces the costs associated with unnecessary chest X-rays, chemoprophylaxis, toxic side effects, lost productivity, and labor costs resulting from two-step TST testing. Studies show that QFT can reduce the cost of maintaining healthcare worker screening programs by up to 32% (10).
Principle
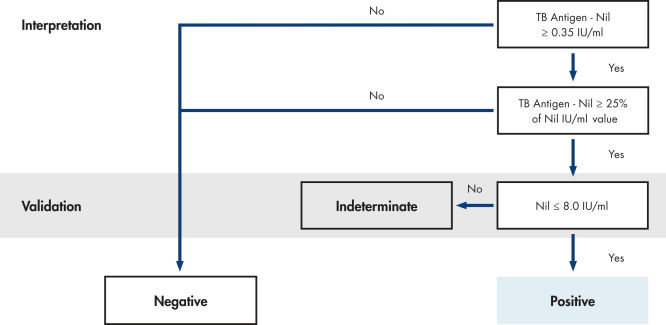
| QFT result | Likelihood of TB infection |
|---|---|
| Positive | Likely |
| Negative | NOT likely |
| Indeterminate | Results are indeterminate for TB antigen responsiveness |
When TB infection can neither be excluded nor confirmed (Indeterminate QFT result), further evaluations are required. Table adapted from QFT Package Insert (1).
See figures
Procedure
- Collect whole blood in specialized QFT blood collection tubes.
- Incubate for 16 to 24 hours at 37°C.
- Detect released IFNγ in harvested plasma by ELISA.
- Analyze results using QFT Analysis Software.
QFT has 3 blood collection tubes (Nil, TB Antigen, and Mitogen) — 1 ml of whole blood should be collected into each tube.
Applications
QFT can be used in many clinical and public health settings, including screening for healthcare workers, immigrants, military personnel, those in correctional facilities, and homeless individuals.
QFT can also be used in at-risk populations, such as:
- People taking certain medications (e.g., TNF alpha inhibitors)
- Patients with weakened immune systems
- Elderly patients
Supporting data and figures
QuantiFERON-TB Gold interpretation flowchart 1