QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 27204
특징
- 플라스미드 DNA의 품질 및 성능은 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit와 동일함
- QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit에 비해 플라스틱은 최대 22%, 판지는 최대 14% 더 적게 사용
- 100% 소비 후 재활용 플라스틱으로 만든 재사용 가능한 폐기물 튜브
- 표준 완충액 대비 플라스틱을 최대 93% 적게 사용하는 완충액 농축물
제품 세부 정보
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit는 표준 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit의 더 친환경적인 버전입니다. QIAwave Kit는 표준 키트보다 플라스틱은 최대 22%, 판지는 최대 14% 더 적게 사용합니다. 100% 소비 후 재활용 플라스틱으로 만든 폐기물 튜브를 제공하며 이를 검사 절차 내내 재사용할 수 있습니다. QIAwave 완충액은 농축물로 제공되므로 병당 플라스틱의 양을 최대 93%까지 줄일 수 있습니다. 종이를 절약하기 위해 키트 내에 인쇄된 프로토콜은 들어있지 않습니다. 리소스 목록에서 프로토콜을 다운로드하거나, 키트 상자 안에 있는 QR 코드를 스캔하여 프로토콜을 확인할 수 있습니다. QIAwave Kit의 키트 포장과 구성품이 표준 키트와 달라 보일 수 있지만, 이는 표준 키트와 마찬가지로 사용하기 쉬우며 화학적 특성과 성능이 동일합니다.
용해 제조한 완충액을 보관하려면 멸균 유리병이 필요합니다.
My Green Lab과의 파트너십을 통해 이 키트가 환경에 미치는 영향도 평가했습니다. My Green Lab ACT 라벨은 몇 가지 지속 가능성 기준에 따라 제품을 평가하고 점수를 매길 수 있도록 설계되었습니다. 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
• 제조
• 책임 있는 화학물질 관리
• 제품 및 포장재 내 지속 가능한 재료
• 수명이 다한 포장재 폐기
제품은 1점부터 10점까지 점수가 매겨지며, 에너지와 물 소비량은 각각 kWh 또는 갤런당 1점씩 점수가 매겨집니다. 점수가 낮을수록 환경에 미치는 영향이 적다는 의미입니다. 그림 'QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit ACT 환경 영향 지수 라벨 US 50/ 250, EU 50/ 250, UK 50/ 250'을 참고하세요.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit는 형광 및 방사성 염기서열 분석 및 클로닝 등 일상적인 분자 생물학 용도로 사용할 최대 20μg의 고순도 플라스미드 또는 코스미드 DNA를 분리하도록 설계되었습니다. QIAprep 고수율 보조 프로토콜을 사용하면 더 높은 수율(최대 30μg)을 얻을 수 있습니다. 최적의 결과를 얻으려면 이 키트를 QIAvac 24 Plus와 함께 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
그림 참조
 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
성능
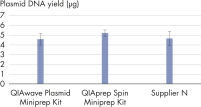
화학적 특성이 동일하므로 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit와 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit의 성능은 동일합니다. 또한 두 키트 모두 경쟁사의 키트보다 성능이 뛰어난 것으로 나타났습니다(그림 ' QIAwave Kit 성능' 참고).
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit를 사용하면 PCR, 염기서열 분석, 클로닝 등 일상적인 분자 생물학 용도로 사용할 최대 20μg의 분자 생물학 등급 플라스미드 DNA 또는 코스미드 DNA를 정제할 수 있습니다.
QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼은 다용도로 사용할 수 있어 마이크로 원심분리기, 진공 매니폴드 또는 QIAcube Connect에서 사용할 수 있습니다(그림 'QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼 취급 옵션 마이크로 원심분리기, 진공 매니폴드, 자동화 시스템' 참고). 진공 절차로 취급이 더 간편해지고 샘플 처리 속도가 더 빨라집니다. QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼은 QIAvac 24 Plus 또는 루어 커넥터가 있는 기타 상용 매니폴드를 사용하여 진공 처리할 수도 있습니다.
| 형식 | 스핀 컬럼 |
| 정제 모듈 | QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼 |
| 처리량 | 샘플 1~24개 |
| 준비 시간 | 30분 내 24개 미니프렙 |
| 필요 장비 | 마이크로 원심분리기 또는 진공 매니폴드, QIAcube Connect를 사용하여 완전히 자동화 가능 |
| 용해물 클리어링 | 원심분리 |
| 컬럼 용기 용량 | 800µL |
| 최소 용출 완충액 용량 | 50µL |
| High-copy 플라스미드의 배양액 용량 | 1~5mL |
| Low-copy 플라스미드/코스미드의 배양액 용량 | 1~10mL |
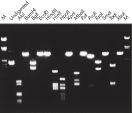
정제된 DNA는 제한효소 처리(restriction digestion)에 사용할 수 있습니다(그림 ' 다양한 제한 효소를 이용한 완전 소화' 참조).
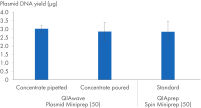
또한 붓거나 피펫팅하여 준비한 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) 완충액을 사용하여 얻은 플라스미드 DNA 수율과 표준 완충액인 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50)를 사용하여 얻은 플라스미드 DNA 수율을 비교했습니다. 두 방법 모두 그림 ' 완충액 농축물 취급'에서 볼 수 있듯이 수율이 비슷합니다.
그림 참조
원리
QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼에는 고농도 카오트로픽 이 있을 때 최대 20µg DNA에 결합하는 고유한 실리카 막이 있으며, 적은 용량의 저염 완충액으로 용출이 가능합니다. QIAprep 막 기술을 사용해 시간이 오래 걸리는 페놀-클로로폼 추출 및 알코올 침전 과정을 거치지 않아도 되며, 느슨한 레진 및 슬러리와 관련된 문제와 불편을 해소할 수 있습니다. QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼에서 용출한 고순도 플라스미드 DNA는 침전, 농축 또는 탈염할 필요가 없어 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
절차
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep을 사용한 DNA 플라스미드 정제는 단순한 결합-세척-용출 절차를 따릅니다(흐름도 ' QIAwave plasmid Miniprep 절차' 참고).
1. 박테리아 배양액을 용해하고 원심분리를 사용하여 용해물을 맑게 만듭니다.
2. 맑아진 용해물을 QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼에 추가합니다. 이 시점에서 플라스미드 DNA가 실리카 막에 흡착되어 불순물이 씻겨 나갑니다.
3. 그 후 순수한 DNA가 소량의 용출 완충액이나 물로 용출됩니다.
E. coli로부터 플라스미드 DNA를 정제하는 것 외에도, QIAwave Plasmid Mini Kit는 Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Agrobacterium tumefaciens에서 플라스미드 DNA를 정제하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 용도를 위해 프로토콜이 필요한 경우 기술 서비스팀 또는 현지 유통업체로 문의하세요.
QIAwave 완충액은 물이나 에탄올을 첨가하여 쉽게 용해 제조할 수 있는 농축물로 제공됩니다. 자세한 내용은 안내서에서 확인하세요. QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 스핀 컬럼 및 폐기물 튜브는 개별 봉투에 들어 있으며 프로토콜을 시작하기 전에 미리 조립해야 합니다. 시간은 조금 더 걸리지만, 플라스틱 쓰레기를 줄일 수 있습니다.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit는 QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit 프로토콜을 사용하여 QIAcube Connect에서 자동화할 수 있습니다.
그림 참조
응용 분야
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit는 다음과 같은 대부분의 용도로 사용하기에 적합한 고순도 DNA를 재현 가능한 수율로 제공합니다.
- PCR
- 제한효소 처리(Restriction digestion)
- 결찰(ligation) 및 형질전환
- 염기서열 분석
- 스크리닝
지원되는 데이터 및 수치
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
This ACT environmental impact factor label evaluates and scores the QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) for plasmid DNA isolation on several sustainability criteria. Scores are 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which is scored as 1 point per kWh. or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) has a 36.8% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50).

Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | 형광 및 방사성 염기서열 분석(모세관 염기서열 분석 포함), ligation, 클로닝, 형질전환 등 |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Culture volume/starting material | 1–10 mL culture volume |
| Elution volume | 50 µL (minimal) |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or prep per run | <30 minutes |
| Yield | <20 ug |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1–24 samples per run |
| Number of preps per run | 1–24 samples per run |