✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 52304
✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
특징
- High-quality의 신속한 분리 정제, ready-to use DNA
- Organic extraction 또는 alcohol precipitation 불필요
- 효율이 높고 결과가 일정함
- 정확한 downstream applications을 위해 inhibitor와 contaminant를 완벽히 제거함
제품 세부 정보
The QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit provides silica-membrane-based purification of cellular RNA from up to 1.5 ml of fresh, whole human blood stabilized with any common anticoagulant, such as citrate, heparin, or EDTA. After homogenization using the QIAshredder spin column, a fast spin-column procedure simplifies RNA purification. Purification can be fully automated on the QIAcube.
성능
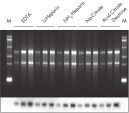
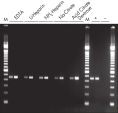
The QIAamp procedure completely removes RNases, contaminants, and enzyme inhibitors, yielding high-quality RNA suitable for any downstream application (see figures " High-quality RNA for northern analysis" and " Reliable RT-PCR analysis").
The QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit provides the highest-quality RNA with minimum copurification of DNA. However, as with any RNA purification method, some DNA contamination can be expected. For certain RNA applications that are sensitive to very small amounts of DNA, it may be necessary to remove any remaining DNA. In these cases, the QIAGEN RNase-Free DNase Set provides convenient on-column DNase treatment of RNA samples during QIAamp RNA procedures.
그림 참조
원리
The QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit provides purification of cellular RNA using silica-membrane technology. No phenol–chloroform extraction is required. RNA binds specifically to the QIAamp silica-gel membrane while contaminants pass through. PCR inhibitors, such as divalent cations and proteins, are completely removed in two efficient wash steps, leaving pure RNA to be eluted in either water or a buffer provided with the kit.
QIAamp technology yields total cellular RNA from fresh whole blood and other sample sources that is ready to use in RT-PCR and blotting procedures. QIAamp sample preparation technology is fully licensed.
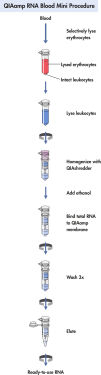
절차
그림 참조
응용 분야
The QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit is designed for isolation of cellular RNA from up to 1.5 ml of fresh, whole human blood stabilized with any common anticoagulant, such as citrate, heparin, or EDTA. In addition, total cellular RNA can be isolated from tissue samples.
지원되는 데이터 및 수치
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini procedure.
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | PCR, real-time PCR, microarray |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl |
| Main sample type | Whole blood, tissue |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | Cellular RNA |
| Sample amount | 50–1.5 ml |
| Format | Spin columns |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation) |
| Time per run or per prep | <1 hour |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Yield | 1–5 µg |