✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
Effectene Transfection Reagent (1 ml)
Cat. No. / ID: 301425
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
特徴
- 血清存在下でも高いトランスフェクション効率
- 少量のDNAで効果的なトランスフェクション
- 他のトランスフェクション試薬に比べて低い細胞毒性
- ハイスループットのスクリーニングに最適
製品詳細
Effectene Transfection Reagentは、様々な細胞株へのDNAトランスフェクション用非リポソーム系脂質の試薬です。Effectene Transfection Reagentは、細胞毒性が非常に低いため初代細胞のような感受性の高い細胞株へのトランスフェクションに最適です。
パフォーマンス
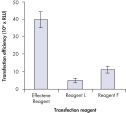
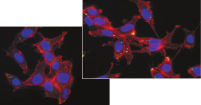
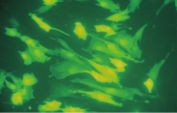
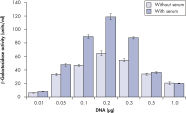
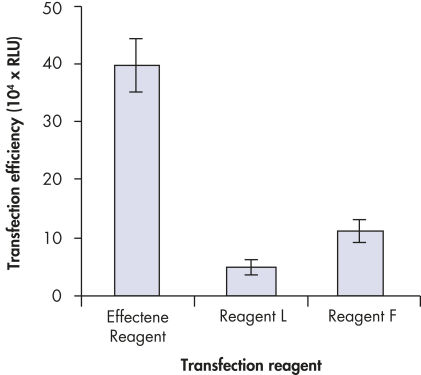
プラスミドDNAのトランスフェクション効率は、Effectene Transfection Reagentが推奨される調製法で用いられる場合、他の試薬よりも高くなります(図" Effectene Reagentによる高トランスフェクション効率")。Effectene Transfection Reagentは、感度の高い細胞株にオリゴヌクレオチドをトランスフェクションする場合に適しており(図" Effectene Reagentによるオリゴヌクレオチドのトランスフェクション")、特に初代培養細胞に効果的です(図" 初代細胞における40%のトランスフェクション効率")。Effectene Reagentによって、多くの細胞株および初代細胞のトランスフェクションが成功しています。細胞型特異的トランスフェクションプロトコールをご用意しています。Effectene Reagentを用いたトランスフェクションは、血清存在下で行なえる上、必要なDNA量も少量(図" 血清、DNA量とトランスフェクション効率の相互関係")なため、細胞毒性を最小限に抑えることが可能です。
創薬などの分野における組み換えDNAテクノロジーの使用により、ハイスループットトランスフェクションの必要性がますます増加しています。Effectene Reagentを用いたトランスフェクションでは、必要なDNA量が少量で済み、操作手順も簡単です。さらにトランスフェクション複合体を除去する必要がないので、ハイスループットのスクリーニングに最適です。Effectene Transfection Reagentはバルクサイズも購入可能です。
図参照
原理
Effectene Transfection Reagentは、トランスフェクション効率を高めるために特殊なDNA凝縮エンハンサーと至適化されたバッファーを組み合わせた斬新な非リポソーム系脂質の試薬です。真核細胞へのDNA導入を特に効果的にするため、エンハンサーによりDNA分子を凝縮し、続いてEffectene Reagentの陽イオン脂質でコーティングします。この特長により、トランスフェクション複合体形成の再現性が特に優れています。
操作手順
Effectene製法には2つのステップがあります。まず効率的にDNAを凝縮するために最適な塩濃度のバッファーとEnhancerをDNAとミックスします。インキュベーション時間はわずか2~5分です。その後、Effectene Reagentを添加し、さらに5~10分インキュベートして、Effectene-DNA複合体を形成させます。複合体に培養液(血清および抗生物質を含む)をミックスして、細胞に直接添加します。この細胞は、回収および遺伝子発現解析を行なうまでインキュベートします(フローチャート" Effectene Transfection製法")。
図参照
アプリケーション
Effectene Transfection Reagentは、幅広い細胞株のトランジェントあるいはステーブルトランスフェクション試薬として最適です。
裏付けデータと数値
High transfection efficiencies using Effectene Reagent.
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | Plasmid transfection, protein overexpression, reporter studies |
| Technology | Non-liposomal lipid formulation in conjonction with a DNA-condensing enhancer |
| Number of possible transfections | 160 transfections in 12-well plates / 1 ml reagent |
| Cell type | Eukaryotic cells (primary cells and sensitive cells) |
| Features | Non-liposomal lipid formulation, minimal cytotoxicity |
| Transfection type | Transient and stable transfection |
| Controls | Not included |
| Nucleic acid | DNA |