QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 27204
特徴
- QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kitと同様のプラスミドDNAの品質と性能
- QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kitと比べると、プラスチックの使用量が22%以下、段ボールの使用量が14%以下まで減少
- 再使用可能な排液チューブは、消費後にリサイクルされたプラスチックで 100% 製造されています。
- 当社の標準バッファーより93%以下の少ないプラスチックを使う濃縮バッファー
製品詳細
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kitは、当社の標準QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kitで一層環境にやさしいバージョンです。QIAwave Kitでは、当社の標準キットと比べると、プラスチックの使用量が22%以下、段ボールの使用量が14%以下まで減り、消費後にリサイクルしたプラスチックで100%製造された排水チューブが提供され、手順全体で再使用できます。QIAwaveバッファーは、濃縮状態で同梱され、ボトルごとにプラスチックの量を93%以下まで減らせます。紙を節約するため、キットの印刷プロトコールはありません。リソースリストからプロトコールをダウンロードしたり、キットボックス内のQRコードをスキャンしたりできます。当社のQIAwave Kitのキットパッケージとコンポーネントは、違うように見えますが、当社の標準キットとして楽に使用でき、化学薬品と性能は同一です。
再構成したバッファーを保存するため、滅菌ガラスボトルが必要になります。
当社は、My Green Labとパートナーシップを組み、このキットの環境に対する影響も評価しました。My Green Lab ACTのラベルは、以下を含む複数の持続可能性基準について製品を評価し、評点を付けるように設計されています。
• 製造
• 化学的管理の責任
• 製品とパッケージ材料内の持続可能なコンテンツ
• 寿命終了時のパッケージ処理
製品には1から10の評点が付きます。ただし、エネルギーと水の消費は、kWhやガロンごとに1点になります。低い点は、低い環境影響を意味します。「QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit ACT環境影響要因ラベルUS 50/ 250、EU 50/ 250、UK 50/ 250」を参照してください。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kitは、最大20 μg高純度プラスミドやコスミドDNAを分離するように設計され、蛍光および放射性シークエンシングやクローニングなどのルーチン分子生物学アプリケーションに使用できます。QIAprep High-Yield Supplementary Protocolを使い、一層高い収率を達成できます(最大30 μg)。最適な結果を得るには、このキットとQIAvac 24 Plusを併用することが、推奨されます。
図参照
 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
パフォーマンス
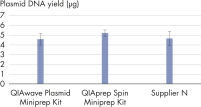
当社のQIAwave Plasmid Miniprep KitおよびQIAprep Spin Miniprep Kitの性能が類似しているのは、化学薬品が同一であるためです。両キットが他社製キットを上回る性能を発揮することも示しました(「 QIAwave Kit performance」を参照)。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kitは、分子生物学グレードのプラスミドDNAまたはコスミドDNAを最大20 μgまで精製し、PCR、シークエンシング、クローニングなどのルーチン分子生物学アプリケーションに使用できます。
QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columnsは、マイクロ遠心機、真空マニホールド、QIAcube Connectで使える多彩な機能が装備されています(「QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column取り扱いオプション、 マイクロ遠心機、 真空マニホールド、 自動システム」の図を参照)。真空手順は、取り扱いが楽で、サンプル処理が迅速になります。QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columnsでは、QIAvac 24 Plusや、他の市販マニフォールド(ルアーコネクター付き)を使って真空処理することもできます。
| フォーマット | スピンカラム |
| 精製モジュール | QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns |
| スループット | 1~24サンプル |
| 調製時間 | 24ミニプレップを30分で |
| 必要な装置 | マイクロ遠心機または真空マニホールド。QIAcube Connectを使用して完全に自動化が可能 |
| 溶解物除去 | 遠心分離 |
| カラムリザーバーの容量 | 800 µL |
| 最小溶出バッファー量 | 50 µL |
| 高コピープラスミドの培養液量 | 1~5 mL |
| 低コピープラスミド/コスミドの培養液量 | 1~10 mL |
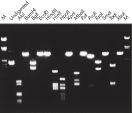
精製したDNAは、制限消化に使用できます(図「 さまざまな制限酵素による完全消化」参照)。
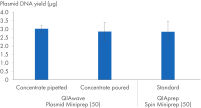
注いでピペッティングする操作で精製したQIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit(50)バッファーと、QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit(50)標準バッファーを使い、取得したプラスミドDNA収率を比べました。両方法は、類似する収率になります(「 濃縮バッファーの取り扱い」の図を参照)。
図参照
原理
QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columnsには、高濃度カオトロピック塩存在下で最大20 μgのDNAを結合し、少量の低塩バッファーで溶出が可能な独自のシリカメンブレンが含まれています。QIAprepメンブレン技術により、時間のかかるフェノール-クロロホルム抽出やアルコール沈殿、樹脂の緩みやスラリーによる問題や不都合が解消します。QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columnsから溶出される高純度プラスミドDNAは、沈殿、濃縮、脱塩の必要がなく、すぐに使用できます。
操作手順
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprepを使うDNAプラスミド精製は、結合、洗浄、溶出のシンプルな手順です(フローチャート「 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep」を参照)。
1. 細菌培養を溶解し、遠心分離を使って溶解物をクリアします。
2. クリアした溶解物をQIAprep 2.0スピンカラムに追加します。この時、プラスミドDNAが、シリカメンブレンに吸収され、不純物が洗い流されます。
3. 次に、少量の溶出バッファーまたは水に、純DNAを溶出します。
E. coliからのプラスミドDNA精製に加えて、QIAwave Plasmid Mini Kitは、Saccharomyces cerevisiaeと、Bacillus subtilis、Agrobacterium tumefaciensからのプラスミドDNA製にも使用できます。このようなアプリケーションについてプロトコールを要する場合は、当社のテクニカルサービスチームまたは最寄りの代理店にお問い合わせください。
QIAwaveバッファーは、水および/またはエタノールを追加し、容易に再構成できる濃縮状態で同梱されます。詳細については、ハンドブックをご確認ください。QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columnsおよび排水チューブは、各バッグに入っており、プロトコールを始める前に組み立てる必要があります。少し時間がかかりますが、プラスチック廃棄物を削減できます。
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kitは、QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kitプロトコールを使い、QIAcube Connectで自動化できます。
図参照
アプリケーション
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kitは、以下のようなほとんどのアプリケーションに適した再現性のある収量の高純度DNAを提供します。
- PCR
- 制限酵素処理
- ライゲーションと形質転換
- シークエンシング
- スクリーニング
裏付けデータと数値
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
This ACT environmental impact factor label evaluates and scores the QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) for plasmid DNA isolation on several sustainability criteria. Scores are 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which is scored as 1 point per kWh. or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) has a 36.8% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50).

Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | 蛍光および放射性シークエンシング(キャピラリーシークエンシングを含む)、ライゲーション、クローニング、形質転換など。 |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Culture volume/starting material | 1–10 mL culture volume |
| Elution volume | 50 µL (minimal) |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or prep per run | <30 minutes |
| Yield | <20 ug |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1–24 samples per run |
| Number of preps per run | 1–24 samples per run |