✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 69104
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Pure DNA, free from contaminants and enzyme inhibitors
- Rapid extraction of ready-to-use DNA
- No organic extraction, no ethanol precipitation
Product Details
The DNeasy Plant Kits provide fast and easy silica-based DNA isolation from plant samples in spin column format. Typical yields are 3–260 μg of high-quality DNA, depending on the samples used (e.g., wheat, maize, Arabidopsis, tomato, tobacco) and binding capacity of the DNeasy silica membrane. The DNeasy Plant Kits also provide silica-based DNA purification in a convenient 96-well plate format with typical yields of 1–15 μg DNA, depending on the plant species. DNA isolation from plant tissue is also automatable on the QIAcube Connect
Performance
The DNeasy Plant Kits allow rapid and efficient isolation of high-quality DNA from a wide variety of plant species and tissue types, including the most demanding sources (see table "Selection of plant species processed with DNeasy Kits"). The samples may be fresh, frozen or dried. The optimized DNeasy Plant procedure incorporates the QIAshredder spin column, a unique filtration and homogenization column that efficiently removes cell debris and improves sample handling following lysis.
Selection of plant species processed with DNeasy Kits
| Abies alba (silver fir) | Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) |
| Aesculus hippocastanum (horse chestnut) | Oryza sativa (rice)4 |
| Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) | Pelargonium sp. (geranium)4 |
| Avena sp. (oat) | Petunia sp.4 |
| Brassica napus (oilseed rape) | Pinus sylvestris (Scotch pine), P. brutia5 |
| Brassica oleracea (kohlrabi) | Populus tremula (aspen) |
| Chicorium endivia (chicory) | Pseudotsuga menziesii (Douglas fir) |
| Citrullini lanatus (water melon) | Quercus robur, Q. petrea (oak)6,7 |
| Egeria sp. | Rhododendron sp.2,4 |
| Fagus sylvatica (beech)1 | Rubus idaeus (raspberry) |
| Helianthus spp. (sunflower) | Solanum tuberosum (potato) |
| Hordeum vulgare (barley)2 | Sphagnum palustre (moss) |
| Humulus sp. (hops) | Spinacia oleracea (spinach) |
| Hydrilla sp. | Taxus baccata (yew) |
| Kalanchoe spp. | Triticum aestivum (wheat)4 |
| Lupinus sp. | Ulmus glabra (elm)6 |
| Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato)3 | Vitis spp. (grape)6 |
| Myriophyllum sp. | Zea mays (maize) |
The typical yield is 3–260 μg, with a sample size of up to 1 g wet weight, and an elution volume of 50 μl to 2 ml. DNA yields vary between different species and tissues depending on genome size, ploidy, cell number and tissue sample age.
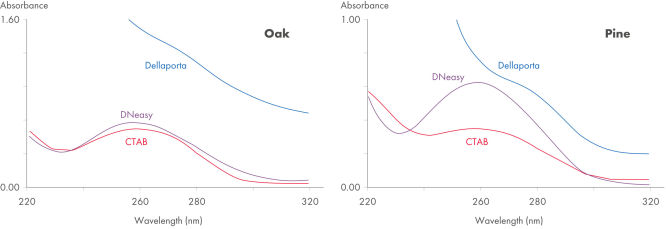
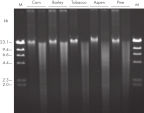
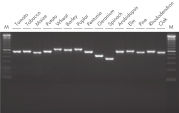
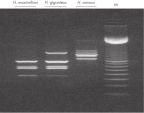
The DNeasy Plant procedure yields pure nucleic acid, free of polysaccharides and other secondary metabolites often copurified using conventional methods. Such impurities can interfere with spectrophotometric readings and inhibit enzymatic reactions. Absorbance scans of DNeasy purified DNA show a symmetrical peak at 260 nm (see figures " DNA purity from oak leaves and pine needles"), confirming that the DNA is free of impurities, including enzyme inhibitors. DNeasy purified DNA is sized up to 40 kb (see figure " Pure DNA (20–25 kb) for restriction analysis"). The purified DNA can be used in a wide range of applications (see figures " PCR analysis" and " RAPD analysis").
See figures
Principle
The DNeasy Plant Kits use advanced silica-membrane technology and simple spin procedures to isolate highly pure total cellular DNA from plant tissues and cells or fungi. The DNeasy technology replaces cumbersome DNA isolation procedures such as CTAB, phenol or chloroform extraction. Alcohol precipitation is also not necessary, since the purified DNA is ready for immediate use.
Procedure
Samples are first mechanically disrupted and then chemically lysed (see flowchart " DNeasy Plant and DNeasy 96 Plant procedures"). RNA is removed by RNAse digestion during lysis. Cell debris, precipitated proteins, and polysaccharides are removed and the sample is homogenized by centrifugation through a QIAshredder spin column. Buffering conditions are adjusted and the lysate is loaded onto the DNeasy Plant Mini spin column. During a brief spin, DNA selectively binds to the silica membrane while contaminants pass through. Remaining contaminants and enzyme inhibitors are removed in one or two efficient wash steps. Pure DNA is then eluted in water or low-salt buffer, ready for use.
See figures
Applications
DNeasy Plant Kits provide purification of ready-to-use DNA from plant samples, including plant cells, plant tissues and fungi.
The DNeasy Plant Kit is designed for:
- DNA extraction from plants and plant-associated microorganisms
- PCR and NGS analysis
- Marker-assisted breeding
- Plant pathogen research
- Studies on genetically modified plants
- Detection of resistance traits
| Features | DNeasy Plant Mini Kit | DNeasy Plant Maxi Kit | DNAeasy 96 Plant Kit | DNeasy Plant Pro Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | PCR, qPCR, blotting, next-generation sequencing | PCR, qPCR, blotting, next-generation sequencing | PCR, qPCR, blotting, next-generation sequencing | PCR, qPCR, blotting, next-generation sequencing |
| Elution volume | 50–200 µl | 500 µl – 2 ml | 100–200 µl | 50–100 µl |
| Format | Spin column | Spin column | 96-well plate | Spin column |
| Main sample type | Plant samples | Plant samples | Plant samples | Plant samples and seeds |
| Bead size | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 5/32” (3.9 mm) ballcone |
| Binding capacity | Up to 50 µg | Up to 500 µg | Up to 50 µg (per well) | Up to 50 µg |
| Processing | Manual | Manual | Manual | Bead beating |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | DNA | DNA | DNA | DNA |
| Sample amount | Up to 100 mg | Up to 1 g | Up to 50 mg | Up to 100 mg |
| Technology | Silica technology | Silica technology | Silica technology | Silica technology |
| Throughput | Varies | Varies | 96 or 192 samples | Varies |
| Time per run or per prep | <1 hour | <2 hours | <2 hours (192 samples) | 45 minutes (24 samples) |
| Typical yield (from 50 mg starting material) | Up to 30 µg | Up to 260 µg | Up to 15 µg | Up to 30 µg |
N.A. = Not applicable
Supporting data and figures
DNA purity from oak leaves and pine needles.
Spectrophotometric scans (220–320 nm) of DNA isolated from pine needles using the method of Dellaporta, CTAB, or the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit. Pure DNA typically shows a symmetrical peak at 260 nm and a smooth profile. Polysaccharides and other secondary metabolites, often copurified with plant DNA isolated using traditional methods, can interfere with OD readings (A260/ A280), leading to errors in determination of concentration and purity.