QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 27204
Caractéristiques
- Qualité et performance de l’ADN plasmidique identiques à celles du QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit
- Jusqu’à 22 % de plastique en moins et jusqu’à 14 % de carton en moins par rapport au QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit
- Tubes de décharge réutilisables constitués à 100 % de plastique recyclé post-consommation
- Les tampon concentrés utilisent jusqu’à 93 % de plastique en moins que nos tampons standard
Détails produit
Le QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit est une version plus respectueuse de l’environnement que notre kit standard QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit. Le QIAwave Kit utilise jusqu’à 22 % de plastique en moins et jusqu’à 14 % de carton en moins que notre kit standard, et propose des tubes de décharge constitués à 100 % de plastique recyclé post-consommation qui peuvent être réutilisés tout au long de la procédure. Les tampons QIAwave se présentent sous une forme concentrée, réduisant ainsi de 93 % la quantité de plastique par flacon. Pour économiser du papier, aucun protocole imprimé n’a été inclus dans le kit. Vous pouvez télécharger les protocoles à partir de la liste des ressources ou scanner le code QR situé à l’intérieur du kit. Bien que l’emballage et les composants de notre kit QIAwave puissent sembler différents, il sont aussi faciles à utiliser que notre kit standard, et la chimie et la performance sont identiques.
Veuillez noter que vous aurez besoin de flacons en verre stériles pour stocker les tampons reconstitués.
En partenariat avec My Green Lab, nous avons également évalué l’impact environnemental de ce kit. Les labels My Green Lab ACT sont destinés à évaluer et à noter les produits selon plusieurs critères de durabilité. Ceux-ci incluent :
• Fabrication
• Gestion responsable des produits chimiques
• Contenu durable dans les produits et les matériaux d’emballage
• Élimination de l’emballage à la fin de sa vie utile
Les produits sont notés de 1 à 10, à l’exception des produits de consommation d’eau et d’énergie à qui l’on attribue 1 point par kWh ou gallon, respectivement. Un faible score signifie un impact environnemental plus faible – voir les figures « Label du facteur d’impact environnemental du QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit ACT US 50/ 250, EU 50/ 250 et UK 50/ 250 ».
Le QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit est conçu pour isoler jusqu’à 20 μg d’ADN plasmidique ou de cosmide très pur pour les applications de biologie moléculaire de routine, notamment le séquençage et le clonage fluorescents et radioactifs. Vous pouvez obtenir des rendements encore plus élevés (jusqu’à 30 μg) à l’aide du Protocole complémentaire à haut rendement QIAprep. Pour des résultats optimaux, nous vous recommandons d’utiliser ce kit avec le QIAvac 24 Plus.
Voir les illustrations
 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
Performances
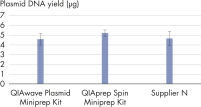
Les performances entre nos QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit et QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit sont identiques car la chimie est la même. Nous avons également démontré que les deux kits sont plus performants que les kits concurrents (voir la figure « Performance du kit QIAwave »).
Le QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit vous permet de purifier jusqu’à 20 μg d’ADN plasmidique ou de cosmide de qualité biologie moléculaire pour les applications de biologie moléculaire de routine telles que la PCR, le séquençage et le clonage.
Les QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns sont si polyvalentes que vous pouvez les utiliser dans des microcentrifugeuses, sur des collecteurs de vide ou sur le QIAcube Connect (voir les figures « Options de manipulation des QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns : microcentrifugeuse, collecteurs de vide et système automatisé »). La procédure sous vide simplifie la manipulation et accélère le traitement des échantillons. Les QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns peuvent également être traitées sous vide avec le QIAvac 24 Plus ou tout autre collecteur commercial avec des raccords luer.
| Format | Colonnes de centrifugation |
| Module de purification | QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns |
| Débit | 1 à 24 échantillons |
| Temps de préparation | 24 minipréparations en 30 minutes |
| Équipement requis | Microcentrifugeuse ou collecteur de vide ; peut être entièrement automatisé avec le QIAcube Connect |
| Nettoyage des lysats | Centrifugation |
| Capacité du réservoir de la colonne | 800 µl |
| Volume minimum du tampon d’élution | 50 µl |
| Volume de culture pour les plasmides à copies élevées | 1 à 5 ml |
| Volume de culture pour les plasmides/cosmides à copies faibles | 1 à 10 ml |
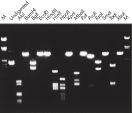
L’ADN purifié peut être utilisé dans la digestion de restriction (voir la figure « Digestion complète avec diverses enzymes de restriction »).
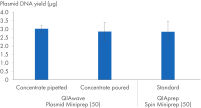
Nous avons également comparé les rendements d’ADN plasmidique obtenus à l’aide du tampon QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50), préparé par versement ou pipettage, et des tampons standard QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50). Les deux méthodes ont permis l’obtention de rendements comparables comme le montre la figure « Manipulation des tampons concentrés ».
Voir les illustrations
Principe
Les QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns contiennent une membrane de silice unique qui lie jusqu’à 20 µg d’ADN en présence d’une forte concentration de sels chaotropiques et permet l’élution dans un faible volume de tampon faiblement salin. La technologie de membrane QIAprep élimine la longue extraction de phénol-chloroforme et la précipitation d’alcool, ainsi que les problèmes et tracas liés aux résines et coulis libres. L’ADN plasmidique de pureté élevée élué dans les QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns est prêt à l’emploi – inutile de précipiter, concentrer ou dessaler.
Procédure
La purification de l’ADN plasmidique avec QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep suit une procédure simple de liaison-lavage-élution (voir le schéma « Procédure QIAwave plasmid Miniprep »).
1. Lysez les cultures bactériennes et nettoyez les lysats par centrifugation.
2. Ajoutez les lysats nettoyés aux QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns. À ce stade, l’ADN plasmidique est adsorbé dans la membrane de silice et les impuretés sont éliminées.
3. L’ADN pur est ensuite élué dans un faible volume de tampon d’élution ou d’eau.
En plus de la purification de l’ADN plasmidique d’E. coli, le QIAwave Plasmid Mini Kit peut être utilisé pour purifier l’ADN plasmidique de Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis et Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Contactez notre équipe de services techniques ou votre distributeur local si vous avez besoin de protocoles pour ces applications.
Les tampons QIAwave se présentent sous une forme concentrée pour une reconstitution facile par ajout d’eau et/ou d’éthanol ; veuillez consulter le manuel pour plus de détails. Les QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns et QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 Waste Tubes sont conditionnés en sachets individuels et doivent être préassemblés avant le début du protocole. Cela prend un peu de temps, mais réduit les déchets plastiques.
Le QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit peut être automatisé sur le QIAcube Connect à l’aide des protocoles du QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit.
Voir les illustrations
Applications
Le QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit fournit des rendements reproductibles d’ADN de pureté élevée adaptés à la plupart des applications, y compris :
- PCR
- Digestion par enzymes de restriction
- Ligature et transformation
- Séquençage
- Dépistage
Données et illustrations utiles
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
This ACT environmental impact factor label evaluates and scores the QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) for plasmid DNA isolation on several sustainability criteria. Scores are 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which is scored as 1 point per kWh. or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) has a 36.8% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50).

Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | Séquençage Séquençage fluorescent et radioactif (y compris le séquençage capillaire), la ligature, le clonage, la transformation, etc. |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Culture volume/starting material | 1–10 mL culture volume |
| Elution volume | 50 µL (minimal) |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or prep per run | <30 minutes |
| Yield | <20 ug |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1–24 samples per run |
| Number of preps per run | 1–24 samples per run |