✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
KRAS Pyro Kit (24)
Cat. No. / ID: 970460
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Comprehensive results in real time
- Accurate quantification of mutations in the KRAS gene
- Easy detection of complex mutations
- Sequence context provides built-in control of the assay
- Flexible post-run analysis
Product Details
The KRAS Pyro Kit is a molecular detection kit for the identification of mutations in the KRAS gene. The kit provides primers and reagents for amplification of the KRAS gene, plus buffers, primers, and reagents for detection and quantification of mutations in real time using Pyrosequencing technology on the PyroMark Q24 System.
Principle
The KRAS Pyro Kit is used for quantitative measurements of mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61 of the human KRAS gene in real time using Pyrosequencing technology on the PyroMark Q24 System. The KRAS gene encodes a protein that plays a critical role in the EGFR signaling cascade. Mutations in the KRAS gene can affect how the protein stimulates these downstream pathways. KRAS is mutated in approximately 30% of all cancer types. Cancers that exhibit a high frequency of KRAS mutation include colorectal cancer (35%) and lung (18%) cancer.
The following mutations are detected:
- Codon 12/13: G12A, G12C, G12D, G12R, G12S, G12V, G13D
- Codon 61: Q61E, Q61H, Q61L, Q61R
Procedure
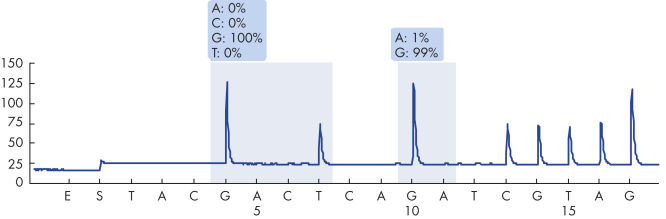
After PCR using primers targeting codons 12/13 and codon 61, the amplicons are immobilized on Streptavidin Sepharose High Performance beads. Single-stranded DNA is prepared, and the corresponding sequencing primers anneal to the DNA. The samples are then analyzed on the PyroMark Q24 System using a run setup file and a run file. The KRAS Plug-in Report should be used to analyze the run. This report ensures that the correct LODs are used and different sequences to analyze are automatically used to detect all mutations. However, the run can also be analyzed using the analysis tool integral to the PyroMark Q24 System (see figure " Pyrogram trace of a GGT to GAT mutation in base 2 of codon 12"). The "Sequence to Analyze" can be then adjusted for detection of rare mutations after the run (see figures " Pyrogram trace of a GGT to TGT mutation in base 1 of codon 12" and " Pyrogram trace of the reanalysis of the sample in the previous figure").
See figures
Applications
The KRAS Pyro Kit enables accurate, quantitative mutation analysis applicable to several fields of research, including cancer research and epigenetics. The kit is used for detecting the most common mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61 of the human KRAS gene.
The following mutations are detected:
- Codon 12/13: G12A, G12C, G12D, G12R, G12S, G12V, G13D
- Codon 61: Q61E, Q61H, Q61L, Q61R
Supporting data and figures
Pyrogram trace of a normal genotype in codons 12 and 13.