QIAseq Targeted RNA Panel (12)
Cat. No. / ID: 333002
Features
- Molecular barcodes remove PCR and library construction bias
- Start with only 25 ng of total RNA
- Simple 1 day library construction workflow
- Use with any illumina or Thermo-Fisher NGS instrument
Product Details
QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels have been developed as a Sample to Insight solution for quantitative gene expression profiling using RNAseq. These panels integrate unique molecular indices (UMIs) and a two-stage PCR-based library preparation to deliver unbiased and accurate quantification from human, mouse and rat samples. QIAseq Targeted Panels are wet-bench verified to ensure the highest quality of results.
QIAseq Targeted RNA Indices are for indexing samples for targeted RNA sequencing and primers necessary for sequencing RNA libraries generated by QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels.
Performance
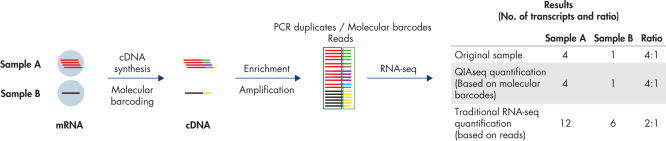
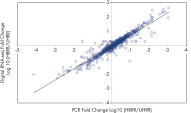
- Accuracy: Innovative UMIs (unique molecular indices) eliminate PCR duplication and amplification bias to deliver the most accurate results (see figure Unbiased and accurate gene quantification).
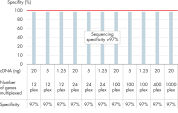
- Specificity: The unique combination of our proprietary primer design algorithm and rigorous testing of every primer assay guarantees high specificity and accurate results (see figure Proprietary primer design delivers gene-specific amplicons – 97% specificity).
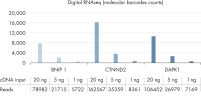
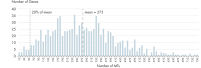
- Uniformity: The QIAseq Targeted RNA Panel workflow has been optimized to deliver highly uniform sequencing results, to ensure sequencing capacity is utilized very efficiently. In fact, UMIs (unique molecular indices) entirely remove PCR bias in RNAseq counting (see figure Unmatched uniformity – 97% of assays are within 20% of median molecular tag counts).
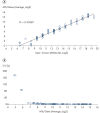
- Reproducibility: The QIAseq Targeted RNA Panel system demonstrates strong correlations across technical replicates, product lots and instruments with correlation coefficients averaging above >0.99, to ensure reliable detection of differences in expression between biological samples
- Sensitivity: Targeted RNA sequencing using UMIs is optimized to deliver highly reliable quantification down to ~100 copies of an RNA target in 25 ng total RNA (see figure Positive results with as little as 0.2 copies of RNA per cell). Low-input protocols allow researchers to start with lower amounts of RNA in smaller volumes.
- Flexibility: QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels combine the power of NGS with the accuracy of qPCR to allow multiplexing of several samples per NGS while delivering cost-effective results (see figure Simple procedure).
See figures
Principle
Traditional RNA sequencing methods suffer from PCR duplication and amplification bias, resulting in inaccurate gene expression analysis. By introducing UMIs (unique molecular indices) before any amplification takes place, QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels are able to eliminate this issue to deliver accurate and digital quantification of genes (see figure Unbiased and accurate gene quantification).
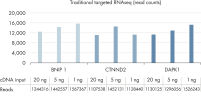
A unique feature of QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels is the set of built-in control assays. The gDNA assays control for any gDNA contamination in the RNA sample to ensure reproducible results. The housekeeping gene (HKG) assays are used to normalize data, thereby making sample-to-sample and run-to-run comparisons possible.
See figures
Procedure
The QIAseq Targeted RNA Panel workflow begins with converting total RNA into cDNA (see figure Simple procedure). The workflow requires minimal RNA input: as little as 25 ng total RNA can be used. No enrichment or rRNA depletion steps are necessary. The molecular indexing step makes use of a gene-specific primer (GSP1) which contains a 12-base UMI in a multiplex primer panel (targeting 12–1000 genes). After the molecular indexing step, the uniquely tagged cDNA is bead purified to remove residual primers, and a PCR is set up with a second pool of gene-specific adapter primers (GSP2) and the RS2 primer, which primes off of a common tag on the GSP1 primers. This reaction insures that intended targets are enriched sufficiently to be represented in the final library. The number of cycles is kept to a minimum to keep PCR-induced variations in amplification to a low level (any variations are easily corrected and accounted for with the UMIs). Another quick cleanup with beads is performed, and a universal PCR is run with RS2 and FS2 primers, which also adds sample-indexing barcodes to each sample. A final cleanup with beads is performed and the library is complete, and ready for quantification and sequencing.
Purchase of QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels provides access to data analysis tools at QIAGEN’s GeneGlobe portal. These include read alignment, data normalization and differential gene expression at no additional costs
See figures
Applications
- Gene expression profiling
- Biomarker research
- Confirmation of whole transcriptome sequencing data
- Confirmation of microarray data
Supporting data and figures
Digital sequencing (molecular barcodes) principle
QIAseq Targeted RNA Panels use a digital sequencing method, whereby a unique 12-base random molecular barcode incorporated into the gene-specific primers (GSP1) is used in the first extension step (after mRNA is converted to cDNA). Thus, every extension event yields a unique combination of molecular barcode and target sequence. At the end of sequencing, the relative amount of each mRNA target is determined by the number of unique molecular barcode-target combinations that were sequenced, thereby eliminating PCR duplicates and amplification bias, resulting in more accurate, unbiased gene expression analysis.