QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 27204
Características
- Calidad y rendimiento del ADN plasmídico idénticos a los del QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit
- Hasta un 22 % menos de plástico y hasta un 14 % menos de cartón en comparación con el QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit
- Tubos de residuos reutilizables fabricados con plástico 100 % reciclado después de su consumo
- Concentrados de soluciones tampón que utilizan hasta un 93 % menos de plástico que nuestros tampones estándar
Detalles del producto
El QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit es una versión más ecológica de nuestro QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit estándar. El QIAwave Kit utiliza hasta un 22 % menos de plástico y hasta un 14 % menos de cartón que nuestro kit estándar y ofrece tubos de residuos fabricados con plástico 100 % reciclado después de su consumo que puede reutilizar durante todo el procedimiento. Las soluciones tampón QIAwave se presentan en forma de concentrados, lo que reduce la cantidad de plástico hasta en un 93 % por botella. Para ahorrar papel, el kit no contiene ningún protocolo impreso. Puede descargar los protocolos de la lista de recursos o escanear el código QR que encontrará en el interior de la caja del kit. Aunque el envase y los componentes de nuestro QIAwave Kit pueden parecer diferentes, es tan fácil de usar como nuestro kit estándar y la composición química y el rendimiento son idénticos.
Tenga en cuenta que necesitará frascos de vidrio estériles para almacenar las soluciones tampón reconstituidas.
Además, en colaboración con My Green Lab, hemos evaluado el impacto medioambiental de este kit. Las etiquetas ACT de My Green Lab están diseñadas para evaluar y puntuar los productos según varios criterios de sostenibilidad. Entre ellos se incluyen:
• Fabricación
• Gestión responsable de los productos químicos
• Contenido sostenible en los productos y materiales de envasado
• Eliminación del envase al final de la vida útil
Los productos se puntúan de 1 a 10, excepto el consumo de energía y agua, que se puntúan con 1 punto por kWh o galón, respectivamente. Una puntuación baja implica un menor impacto medioambiental (consulte las figuras «Etiqueta del factor de impacto medioambiental del QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit ACT US 50/ 250, EU 50/ 250 y UK 50/ 250»).
El QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit está diseñado para aislar hasta 20 μg de ADN plasmídico o cósmido ultrapuro para aplicaciones habituales de biología molecular, que incluyen la secuenciación fluorescente y radioactiva y la clonación. Puede conseguir rendimientos aún mayores (hasta 30 μg) utilizando el QIAprep High-Yield Supplementary Protocol. Recomendamos utilizar este kit con QIAvac 24 Plus para obtener resultados óptimos.
Ver figuras
 QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label US. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label EU. QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (250) ACT environmental impact factor label UK.
Rendimiento
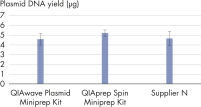
El rendimiento entre nuestro QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit y el QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit es idéntico porque la composición química es la misma. También hemos demostrado que ambos kits superan a los de la competencia (consulte la figura « Rendimiento del QIAwave Kit»).
El QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit permite purificar hasta 20 μg de ADN plasmídico o ADN cósmido de calidad de biología molecular para su uso en aplicaciones habituales de biología molecular como la PCR, la secuenciación y la clonación.
Las QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns son tan versátiles que puede utilizarlas en microcentrifugadoras, en colectores de vacío o en el QIAcube Connect (consulte las figuras «Opciones de manejo de la QIAprep 2.0 Spin Column microcentrifugadora, colectores de vacío y sistema automatizado»). El procedimiento de vacío simplifica la manipulación y acelera el procesamiento de las muestras. Las QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns también pueden procesarse al vacío con el uso de QIAvac 24 Plus o con cualquier otro colector con conectores luer.
| Formato | Columnas de centrifugación |
| Módulo de purificación | QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns |
| Rendimiento | 1-24 muestras |
| Tiempo de preparación | 24 minipreparaciones en 30 minutos |
| Equipamiento necesario | Microcentrifugadora o colector de vacío; completamente automatizables con el uso del QIAcube Connect |
| Aclaramiento de lisados | Centrifugación |
| Capacidad del depósito de la columna | 800 µl |
| Volumen mínimo de la solución tampón de elución | 50 µl |
| Volumen de cultivo para plásmidos de alto número de copias | 1-5 ml |
| Volumen de cultivo para plásmidos/cósmidos de bajo número de copias | 1-10 ml |
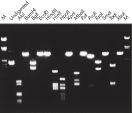
El ADN purificado se puede utilizar para digestión de restricción (consulte la figura “ Digestión completa con varias enzimas de restricción”).
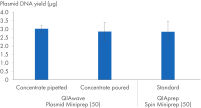
También hemos comparado los rendimientos de ADN plasmídico obtenidos utilizando la solución tampón QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50), preparado por decantación o pipeteo, y las soluciones tampón estándar QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50). Ambos métodos ofrecen rendimientos comparables, como se muestra en la figura « Manipulación de concentrados de soluciones tampón».
Ver figuras
Principio
Las QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns contienen una membrana de sílice única que une hasta 20 μg de ADN en presencia de una concentración alta de sal caotrópica y permite la elución en un volumen pequeño de solución tampón de baja salinidad. La tecnología de membrana de QIAprep elimina la extracción con fenol y cloroformo y la precipitación con alcohol que requieren de mucho tiempo, así como los problemas e inconvenientes relacionados con las resinas sueltas y los residuos pastosos. El ADN plasmídico ultrapuro eluido a partir de las QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns está inmediatamente listo para su uso y no es necesario precipitarlo, concentrarlo o desalarlo.
Procedimiento
La purificación de plásmidos de ADN utilizando el QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep sigue un sencillo procedimiento de unión, lavado y elución (consulte el diagrama « Procedimiento QIAwave plasmid Miniprep»).
1. Lise los cultivos bacterianos y limpie los lisados mediante centrifugación.
2. Añada los lisados limpios a las QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns. En este punto, la membrana de sílice absorbe el ADN plasmídico y se eliminan las impurezas.
3. El ADN puro se eluye en un volumen pequeño de solución tampón de elución o agua.
Además de usarse para la purificación de ADN plasmídico de E. coli, el QIAwave Plasmid Mini Kit se puede utilizar para purificar el ADN plasmídico de Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis y Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Póngase en contacto con nuestro equipo de servicio técnico o con su distribuidor local si necesita protocolos para estas aplicaciones.
Las soluciones tampón QIAwave se presentan como concentrados que pueden reconstituirse fácilmente añadiendo agua o etanol; consulte el manual de uso para obtener más información. Las QIAwave QIAprep 2.0 Spin Columns y los tubos de residuos vienen en bolsas individuales y deben montarse previamente antes de iniciar el protocolo. Esto lleva un poco más de tiempo, pero reduce los residuos de plástico.
El QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit puede automatizarse en el QIAcube Connect utilizando los protocolos del QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit.
Ver figuras
Aplicaciones
El QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit aporta rendimiento reproducible de ADN ultrapuro apto para su uso en la mayoría de las aplicaciones, incluidas:
- PCR
- Digestión de restricción
- Ligación y transformación
- Secuenciación
- Cribado
Datos y cifras de respaldo
QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
This ACT environmental impact factor label evaluates and scores the QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) for plasmid DNA isolation on several sustainability criteria. Scores are 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which is scored as 1 point per kWh. or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave Plasmid Miniprep Kit (50) has a 36.8% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (50).

Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | Secuenciación fluorescente y radioactiva (incluida la secuenciación capilar), ligación, clonación, transformación, etc. |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Culture volume/starting material | 1–10 mL culture volume |
| Elution volume | 50 µL (minimal) |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or prep per run | <30 minutes |
| Yield | <20 ug |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1–24 samples per run |
| Number of preps per run | 1–24 samples per run |