PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Concentrate (150 ml)
Cat. No. / ID: 765512
Features
- Preservation of both morphology and biomolecules
- Tissue can be stored and archived for later processing
- RNA, miRNA, DNA, and/or proteins from one sample
Product Details
PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Concentrate is only to be used in conjunction with tissue specimens previously fixed in PAXgene Tissue FIX.
Performance
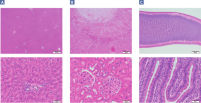
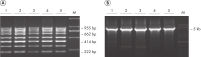
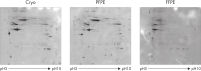
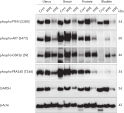
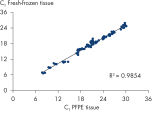
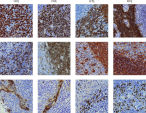
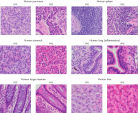
The fixation and stabilization method preserves tissue morphology and the integrity of nucleic acids without destructive crosslinking and degradation found in formalin-fixed tissues (see figure " Preservation of tissue morphology").
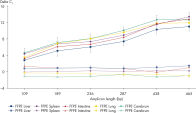
When fixed tissue is stored in PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER, the nucleic acids, proteins, and morphology of the tissue sample are stable for up to 7 days at room temperature (15–25°C) or for up to 4 weeks at 2–8°C. Tissue samples can even be stored in the PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER for longer periods at –20°C (–15°C to –30°C) or –80°C (–65°C to –90°C) without negative effects on the morphology of the tissue or the integrity of the nucleic acids.
Specifications for storage conditions in PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER were determined using animal tissues.
See figures
Principle
The methods for tissue fixation currently used in traditional histology are of limited use for molecular analysis. Fixatives that contain formaldehyde crosslink biomolecules and modify nucleic acids and proteins. Such crosslinks lead to nucleic acid degradation during tissue fixation, storage, and processing. Since they cannot be removed completely, the resulting chemical modifications can cause inhibition in downstream applications, such as quantitative PCR or RT-PCR. To enable both molecular and traditional pathology testing from the same specimen, a method is needed to stabilize molecular content and preserve morphology.
To meet this need, PreAnalytiX has developed the PAXgene Tissue System. The system consists of a fixation reagent (PAXgene Tissue FIX), a stabilization reagent (PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER), prefilled containers for tissue collection, storage, and transportation, and kits for purification of RNA, DNA, or total RNA, including miRNA. In addition, supplementary protocols for protein purification and other applications are available in the 'Resources' section of this page or at www.preanalytix.com.
PAXgene Tissue reagents in prefilled containers and PAXgene Tissue Kits provide a complete preanalytical solution for collection, fixation, and stabilization of tissue, and purification of high-quality nucleic acids for molecular research analysis.
Procedure
Applications
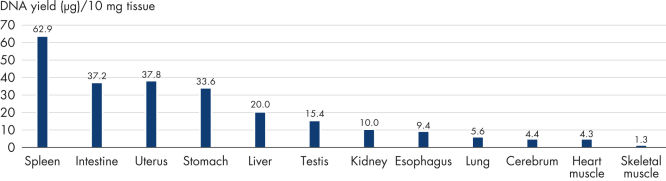
Supporting data and figures
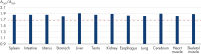
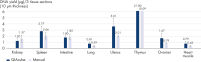
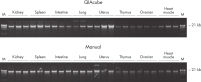
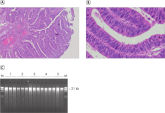
Yield of high-quality, high molecular weight DNA from 12 different PAXgene Tissue-fixed (PF) tissue types, processed on the QIAcube.