✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Allprotect Tissue Reagent (100 ml)
Cat. No. / ID: 76405
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- No need for liquid nitrogen or dry ice
- Immediate, convenient stabilization of harvested tissues
- Long-term storage of tissues for later analysis
- Standardized sample preparation for systems biology
Product Details
Performance
See figures
Principle
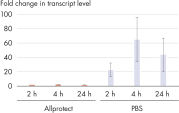
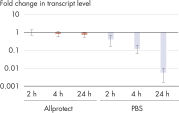
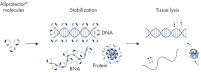
Freshly harvested tissue is submerged in Allprotect Tissue Reagent to immediately preserve the in vivo profile of DNA, RNA, and protein. Tissue samples in Allprotect Tissue Reagent are stabilized for long-term storage without freezing and can be stored at room temperature for up to 7 days or at 2–8°C for up to 12 months.
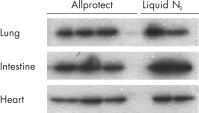
The reagent is part of QIAGEN’s range of sample technologies for systems biology, and can be used in combination with the AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit, which allows simultaneous purification of DNA, RNA, and protein from the same precious sample. Allprotect stabilized tissues are also compatible with QIAGEN kits for purification of DNA, RNA, or protein, such as DNeasy, QIAamp, RNeasy, and Qproteome Kits. Functional protein for enzyme assays can be purified from Allprotect stabilized tissues using the Qproteome Mammalian Protein Prep Kit. There is no need to split the sample into 3 prior to purification, allowing maximum recovery of DNA, RNA, and protein. In addition, no organic solvents such as phenol and acetone are required. DNA, RNA, and protein are all prepared from the same source, eliminating the variation inherent in preparing these analytes from different samples.
QIAGEN sample technologies for individual purification of DNA, RNA, and protein are also available (see table). These include the Qproteome Mammalian Protein Prep Kit, which allows purification of functional protein from Allprotect stabilized tissues. Protein purified from Allprotect stabilized tissue with the Qproteome Mammalian Protein Prep Kit is suitable for all downstream applications.
| Analytes purified | Recommended kit |
|---|---|
| Genomic DNA, total RNA, and total protein | AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit |
| Genomic DNA and total RNA | AllPrep DNA/RNA Micro Kit AllPrep DNA/RNA Mini Kit AllPrep DNA/RNA/miRNA Universal Kit |
| Genomic DNA | DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit QIAamp DNA Mini Kit |
| Total RNA | RNeasy Plus Micro Kit* (for small tissue samples) RNeasy Mini Kit (for easy-to-lyse tissues) RNeasy Plus Mini Kit* (for easy-to-lyse tissues) RNeasy Fibrous Tissue Mini Kit (for fibrous tissues) RNeasy Lipid Tissue Mini Kit (for fatty tissues) RNeasy Microarray Tissue Mini Kit (for tissue samples for microarray analysis) |
| Total protein | Qproteome Mammalian Protein Prep Kit |
Procedure
Freshly harvested tissue is submerged in Allprotect Tissue Reagent to immediately stabilize DNA, RNA, and protein (see figure " Mechanism of Allprotect stabilization"). Stabilization takes place at room temperature, eliminating the use of hazardous liquid nitrogen or dry ice. Immediate stabilization of harvested tissues in Allprotect Tissue Reagent preserves the in vivo profile of DNA, RNA, and proteins, enabling reliable downstream analysis.
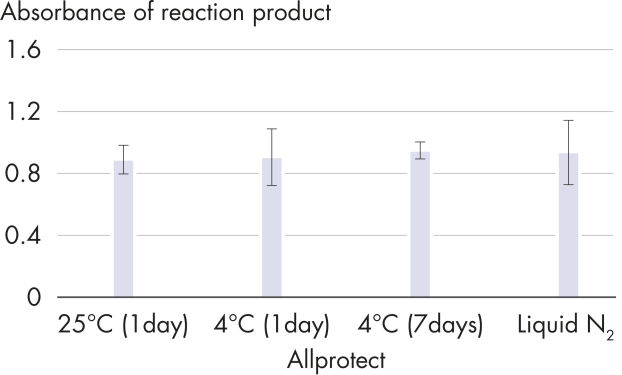
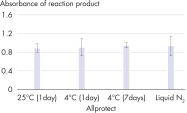
Tissues stabilized in Allprotect Tissue Reagent can be stored at room temperature for up to 7 days or at 2–8°C for up to 12 months without showing any degradation of DNA, RNA, and protein. For longer storage, stabilized tissues can be archived at –20°C or –80°C.
See figures
Applications
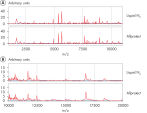
DNA, RNA, and protein can be simultaneously purified from Allprotect stabilized tissues using the AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit. The combination of Allprotect and AllPrep sample technologies standardizes sample preparation for systems biology. Genomic DNA and total RNA purified using the AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit deliver optimal results in all downstream applications. These include real-time PCR and RT-PCR analyses. Protein purified from Allprotect stabilized tissue is denatured and suitable for SDS-PAGE and western blotting.
Supporting data and figures
Preservation of protein activity.