✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit (24)
Cat. No. / ID: 971470
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Compliance with EU IVD Directive 98/79/EC
- Comprehensive results in real time
- Accurate quantitation of cancer-related BRAF gene mutations
- Easy interpretation of complex sequence information
Product Details
Performance
Linearity
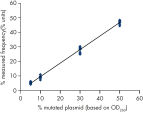
Linearity was determined using mixtures of plasmids carrying the wild type or mutant sequence for the mutation V600E (GTG->GAG) in codon 600 of the BRAF gene (see figure " Linearity of V600E mutation"). The plasmids were mixed in proportions to give four levels of mutation (5, 10, 30, and 50%). Each mixture was analyzed with three different lots of the therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit in three Pyrosequencing runs with three replicates each.
The results were linear within an allowable nonlinearity of 5 % units in the tested range of 5 to 50% mutation level.
Precision
The precision data allows the determination of the total variability of the assays and was obtained at three different levels by analysis of the above mentioned plasmid mixtures with three replicates each.
Repeatability (intra-assay and inter-batch variability) was calculated based on the data for determination of linearity (three runs on the same day using varying lots of the therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit). Intermediate precision (intra-laboratory variability) was determined in three runs within one laboratory on three different days with varying operators, PyroMark Q24 systems, and lots of the therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit. Reproducibility (inter-laboratory variability) was calculated from two runs each in an internal and external laboratory and using varying lots of the therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit.
Precision estimates are expressed as standard deviation of the measured mutation frequencies in % units. The repeatability, intermediate precision, and reproducibility for the mutation V600E (GTG->GAG) in codon 600 was 0.6–2.1, 0.7–1.8, and 0.8–2.1 % units, respectively, in the measured range of 5 to 50% mutation level.
| % mutated plasmid | Repeatability (Mean, SD) | Intermediate precision (Mean, SD) | Reproducibility (Mean, SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5.2, 0.6 | 4.4, 0.7 | 5.1, 0.8 |
| 10 | 9.1, 1.0 | 9.6, 1.0 | 9.6, 1.3 |
| 30 | 28.1, 2.1 | 27.9, 1.8 | 28.3, 2.1 |
| 50 | 46.9, 1.2 | 46.3, 1.5 | 47.9, 1.7 |
See figures
Principle
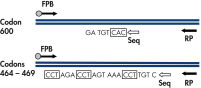
The therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit is used for quantitative measurements of mutations in codons 600 and 464–469 of the human BRAF gene in real time using Pyrosequencing technology on the PyroMark Q24 System. The BRAF gene encodes the kinase v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1, a proto-oncogene that acts downstream of EGFR. Mutations in the BRAF gene are found in 6–8% of all cancers and more frequently in melanoma (50–60%), colorectal cancer (10%), and thyroid (39%) cancers. Approximately 90% of these mutations are V600E substitutions.
The following mutations are detected:
- Codon 600: V600A, V600E, V600G, and V600M
- Codon 464–469: G464E, G464V, G466E, G466V, G469A, G469E, and G469V
Procedure
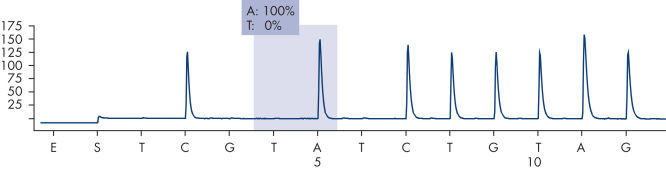
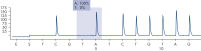
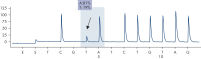
After PCR using primers targeting codon 600 and codons 464–469, the amplicons are immobilized on Streptavidin Sepharose High Performance beads. Single-stranded DNA is prepared, and the corresponding sequencing primers anneal to the DNA. The samples are then analyzed on the PyroMark Q24 System using a run setup file and a run file (see figures " Pyrogram trace of a normal genotype in codon 600", " Pyrogram trace of a normal genotype in codons 464–469", and " Pyrogram trace of a GTG to GAG mutation in base 2 of codon 600"). The "Sequence to Analyze" can be adjusted for detection of rare mutations after the run.
See figures
Applications
The therascreen BRAF Pyro Kit is intended to be used as an aide to identify melanoma or colorectal cancer patients more likely to benefit from treatment with cancer therapies that are selective inhibitors of BRAF. The kit is used for the detection of mutations in codons 600 and 464–469 of the human BRAF gene.
The following mutations are detected:
- Codon 600: V600A, V600E, V600G, and V600M
- Codon 464–469: G464E, G464V, G466E, G466V, G469A, G469E, and G469V
Supporting data and figures
Pyrogram trace of a normal genotype in codon 600.