Rotor-Gene SYBR® Green PCR Demo Kit
For evaluation of Rotor-Gene Q performance
For evaluation of Rotor-Gene Q performance
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 204001
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
The Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit is for use in demonstrating the performance of the Rotor-Gene Q. The kit contains all the necessary reaction components to quantify a genomic DNA target by SYBR Green-based real-time PCR. These include prediluted genomic DNA standards, 2 unknown samples, an optimized master mix, and a primer pair specific for the human G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER) gene. Using the kit, the reliability, reproducibility, and sensitivity of gene quantification with the Rotor-Gene Q can be evaluated.
The Rotor-Gene Q and its unique centrifugal rotary design enables fast and accurate gene quantitation. PCR tubes are placed into a rotor that spins tubes past a single excitation light source and a single detector in a chamber of moving air. This means that there is minimal optical and temperature variation between tubes, enabling high precision in real-time PCR quantification. In addition, as the rotor spins continuously at 400 rpm, high-speed data acquisition is possible.
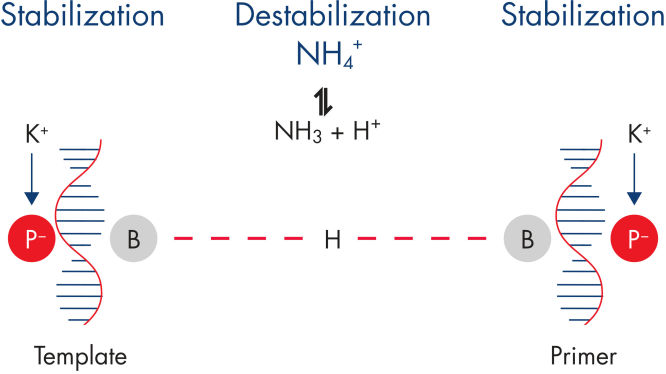
With the Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit, highly specific amplification is assured through a balanced combination of ions that minimizes nonspecific primer annealing (see figure " Specific primer annealing"). Fast cycling without compromising performance is achieved using Q-Bond, a novel PCR additive that enables cycler run times of as low as 45 minutes (see figure " Fast primer annealing").
Using the Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit, SYBR Green-based real-time PCR is carried out to quantify different copy numbers of a genomic DNA target. Each reaction consists of:
The Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit handbook contains 3 protocols. Rotor-Gene users follow either the protocol for manual reaction setup or the protocol for automated reaction setup using the QIAgility. After reaction setup, users then proceed to the protocol for real-time PCR on the Rotor-Gene Q.
Manual pipetting steps can be avoided by using the QIAgility, a compact benchtop instrument that provides rapid, high-precision PCR setup. Mistakes in reaction setup due to human error are reduced and may be eliminated. The QIAgility perfectly complements the combination of the Rotor-Gene Q and Rotor-Gene Kits, enabling easy dispensing of liquids into tubes, strip tubes, and Rotor-Discs.
A standard curve is generated from the CT values obtained from a set of standards (2000, 1000, 500, 250, and 125 copies; each standard is analyzed in quadruplicate). The standard curve is then used to determine the copy number for 2 unknown samples (500 and 250 copies; 24 replicates of each unknown sample are analyzed [when performing manual reaction setup, a minimum of 4 replicates for each unknown sample can be set up instead]). In addition, 4 no template control (NTC) reactions are carried out. Thus, a total of 72 reactions are run at the same time on the Rotor-Gene Q.
The Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit is for use in demonstrating the performance of the Rotor-Gene Q. The kit is also compatible with the Rotor-Gene 3000 or the Rotor-Gene 6000. Using this kit, the accuracy and reproducibility of gene quantification with the Rotor-Gene Q can be evaluated.