✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kit (24)
Cat. No. / ID: 333272
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Compatible with QIAGEN, Illumina, NEB and KAPA stranded RNA-seq library kits
- Provides pan-bacterial 5S/16S/23S rRNA removal from fragmented or full-length RNA, and cytoplasmic and mitochondrial rRNA removal for human, mouse, rat and related species
- Separate reagents for bacteria and HMR (human, mouse and rat) for flexibility in single or dual-seq applications
- Simple procedure works with existing workflows to save time
Product Details
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits are designed for “dual-seq” or “host-pathogen” RNA-seq Library construction. Researchers using QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits for RNA-seq library construction will remove bacterial 5S/15S/23S rRNA and human, mouse and rat cytoplasmic and mitochondrial ribosomal RNA. The reagents for bacterial and HMR rRNA removal are supplied in separate tubes, allowing researchers to optimize their RNA-seq workflows for dual-seq, bacteria or HMR samples.
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits use a novel method to remove highly abundant RNA that is of low scientific value from your RNA-seq libraries. They have been tested with QIAGEN, Illumina, Roche/KAPA and NEB RNA-seq library kits, and are compatible with all major methods of RNA-seq library preparation. The simple 14-minute FastSelect protocol and subsequent bead-based cleanup integrates seamlessly with all common RNA-seq library kits and can be used on fragmented or full-length (non-fragmented) RNA.
Analyze RNA-seq data with ease using the GeneGlobe-integrated RNA-seq Analysis Portal – an intuitive, web-based data analysis solution created for biologists and included with this QIAseq Kit.
We recommend using QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits for rapid, robust strand-specific RNA-seq library preparation for both high-quality and highly fragmented RNA.
Design your own custom QIAseq FastSelect pools to remove any RNAs you wish from your RNA-seq library – take a look at our QIAseq FastSelect Custom RNA Removal Kits.
Want to try the QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kit for the first time? Request a trial kit to evaluate.
Principle
Removing highly expressed, but biologically unimportant RNA transcripts makes NGS more efficient and enables higher sample throughput with higher sensitivity. Furthermore, removal of unwanted RNA species from full length and fragmented RNA samples can be particularly challenging and can result in suboptimal performance.
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits are a pan-bacterial ribosomal RNA (rRNA) removal kit designed to remove 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA, and human, mouse and rat cytoplasmic and mitochondrial ribosomal RNA from complex samples. Our comprehensive rRNA removal reagent has been designed using 16S (nearly 600,000 entries), 23S (nearly 170,000 entries) and 5S rRNA sequences (over 7200 entries). In-silico modeling predicts >95% rRNA removal of all known 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA sequences.
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits can accommodate RNA amounts ranging from as little as 20 ng up to 1 µg, with consistently high performance, and is compatible with low-quality, highly fragmented or high-quality full-length RNA. Since QIAseq FastSelect does not use enzymatic digestion or hybrid-capture procedures, the fast, simple workflow results in reliable rRNA removal and high reproducibility in downstream applications.
Our unique QIAseq FastSelect procedure is significantly faster than existing methods and QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits have been tested with QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB stranded RNA-seq library kits
Procedure
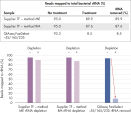
Most RNA removal or depletion strategies associated with RNA-seq library construction are sample pre-treatment strategies involving hybrid-capture or enzymatic removal of unwanted RNA. Our unique QIAseq FastSelect procedure is compatible with QIAGEN, Illumina, KAPA, NEB and other RNA library kits and provides complete rRNA removal in a single, 14-minute inline step (see figure “ QIAseq FastSelect Kit workflow”). This is dramatically faster than alternative RNA depletion kits, which require pre-treatment protocols involving more than 25 steps and 2 hours to complete (see figure QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: rRNA removal).
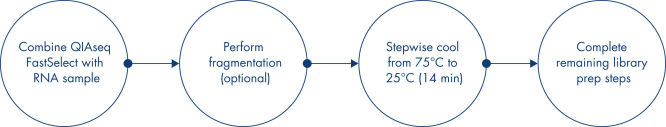
QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits seamlessly integrate with your existing RNA-seq library preparation, providing RNA removal in a single, 14-minute step, which is followed by bead cleanup. Prior to RNA heat fragmentation (which is optional and dependent upon the library preparation kit and sample type), QIAseq FastSelect is directly combined with total RNA and fragmentation buffer. After optional fragmentation, the reaction temperature is stepwise cooled from 75°C to 25°C over 14 minutes, followed by a bead cleanup. The RNA is then ready for reverse transcription.
See figures
Applications
QIAseq FastSelect delivers rapid, reliable RNA removal from full length or fragmented RNA samples from many species. QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits are available in a variety of different formats and sizes to suit your specific applications.
Supporting data and figures
QIAseq FastSelect Kit workflow
Simply add QIAseq FastSelect reagent (rRNA Removal and/or Globin Removal) to your RNA sample, perform fragmentation (if required), then initiate a stepwise cool-down from 75°C to 25°C over 14 minutes. Researchers can then complete the remaining library preparation steps without any additional changes to their workflow. QIAseq FastSelect works with or without RNA fragmentation, providing the flexibility to use FFPE or degraded RNA samples, or high-quality RNA as part of a standard RNA-seq library construction workflow.
QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA HMR Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –Globin Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA/Globin Kit, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA Plant Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA Yeast Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA Worm Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA Fly Kits, QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA Fish Kits and QIAseq FastSelect Epidemiology Kits have been tested with the QIAseq Stranded Total RNA Lib Kit (QIAGEN), TruSeq Stranded (Illumina), NEBNext Ultra II Directional (New England Biolabs) and KAPA RNA HyperPrep (KAPA Biosystems) library preparation kits.